Well-designed buildings retain their form and function for decades. Poorly planned ones deteriorate fast. The difference often lies in how durability is considered—starting with entrances and extending across the entire building envelope.
Durable materials, weather-resistant entryways, and fitted exterior protection help structures withstand wear and environmental exposure. Durable design isn’t just about longevity—it supports structural integrity and visual appearance.
When applied correctly, it allows architects and property owners to protect assets, reduce maintenance costs, and extend the usable life of any facility.
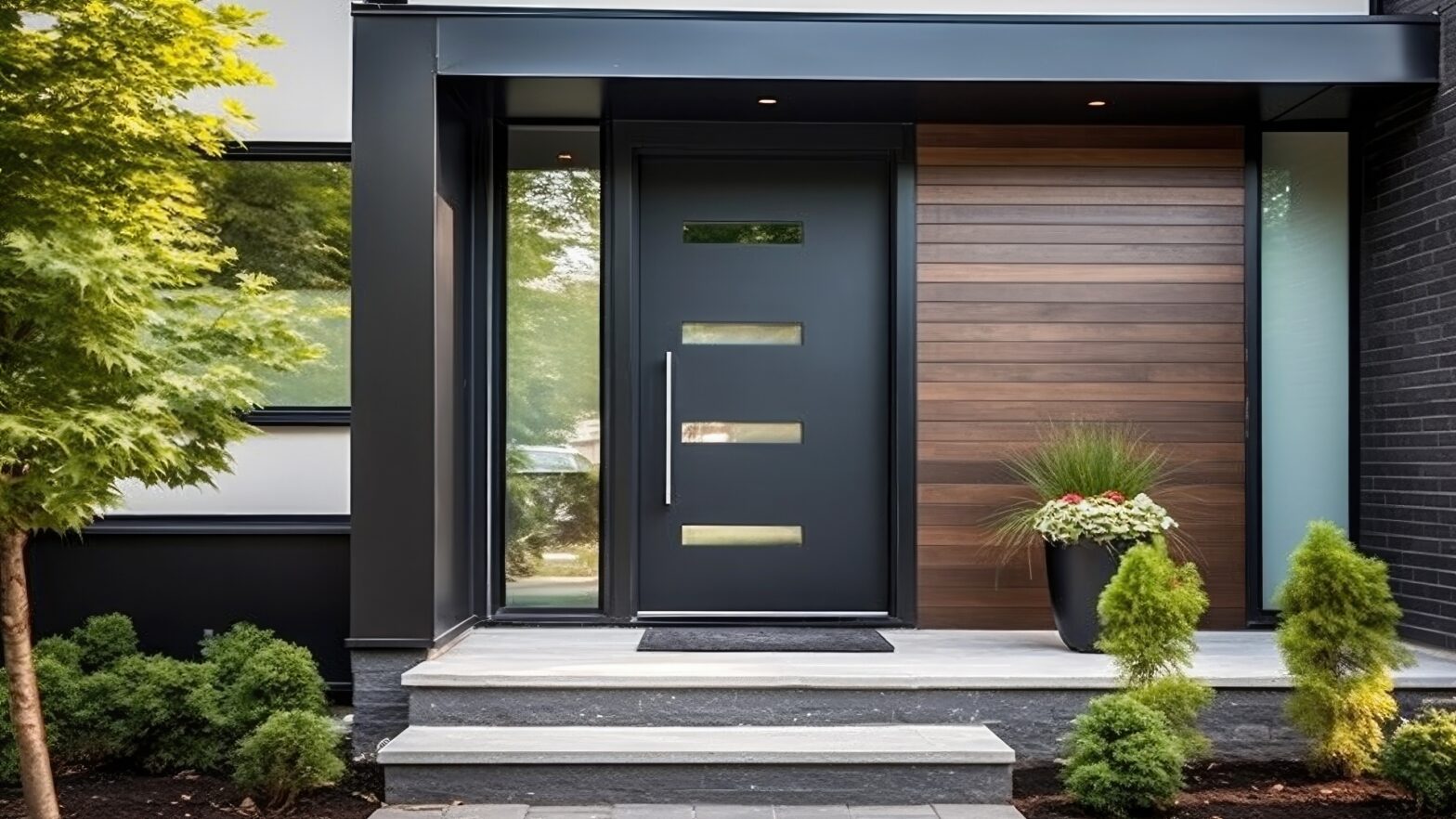
First Impressions Begin With Resilient Entryways
A well-designed entrance serves as both a visual landmark and a protective barrier. It must withstand continuous foot traffic, fluctuating weather, and daily operational pressures—without compromising appearance or function.
Creating a resilient entry begins with robust materials that balance durability with aesthetic value. For instance, precision-engineered custom metal signage can reinforce the entrance while supporting structural integrity.
Key Components of a Long-Lasting Entryway
Quality entrances rely on specific features to maintain performance over time. The following elements form the foundation of a resilient entry system:
- Weather-resistant door frames and fittings to prevent corrosion and heat distortion
- Impact-resistant glazing or reinforced cladding for high-stress interactions
- Effective drainage systems around entry thresholds to prevent water ingress
- Durable, non-slip flooring in areas exposed to heavy use or shifting weather
- Targeted exterior lighting for improved visibility and safer access during low-light hours
Why Entrance Integrity Influences Overall Longevity
The durability of entrance systems contributes directly to the building’s protective envelope. Effective design considers wind load, moisture exposure, and regional climate—factors influencing material wear and long-term performance.
The right structural choices at the entrance can enhance energy efficiency, reduce ongoing maintenance, and set consistent standards for the rest of the building shell.
Well-planned entrance protection ultimately supports broader strategies in exterior resilience and architectural value.
Safeguarding Exteriors With Proven Protective Layers
Exterior elements endure constant exposure to harsh weather, UV rays, chemical pollutants, and airborne debris. These stressors degrade materials over time, compromising structural resilience and aesthetic value.
Adequate exterior protection is a key component of design durability, helping preserve performance and reduce long-term repair costs.
Building an Effective Defence Strategy
A robust exterior defence system integrates several proven technologies and materials, each addressing a specific vulnerability.
Expert designers and contractors often choose solutions that combine moisture control, thermal resistance, and pollutant protection. Proper planning also protects external assets such as parked vehicles and exterior branding.
For example, using durable car covers designed for long-term outdoor exposure helps shield vehicles from UV degradation, weather impacts, and airborne contaminants—supporting a more comprehensive site protection approach.
Key components of a well-rounded exterior protection system include:
- High-grade weather barriers to prevent moisture intrusion
- UV-resistant coatings to minimise solar damage and fading
- Engineered drainage systems for effective water management
- Protective surface treatments to counter pollution build-up
- Use of structural overhangs and shields to reduce direct exposure
Long-Term Value Through Early Action
Investing in external protection from the start helps avoid premature wear and costly repairs. When applied during the design and construction phases, these protective strategies extend the lifecycle of critical components and reduce upkeep requirements.
This forward-thinking approach delivers long-term savings and ensures the building retains functional performance and visual quality well into the future.
| Integrate drainage grates: Install recessed, easy-to-clean drainage grates or trench drains around entrances to redirect runoff and melted snow immediately, preserving interior and structural entry points. |
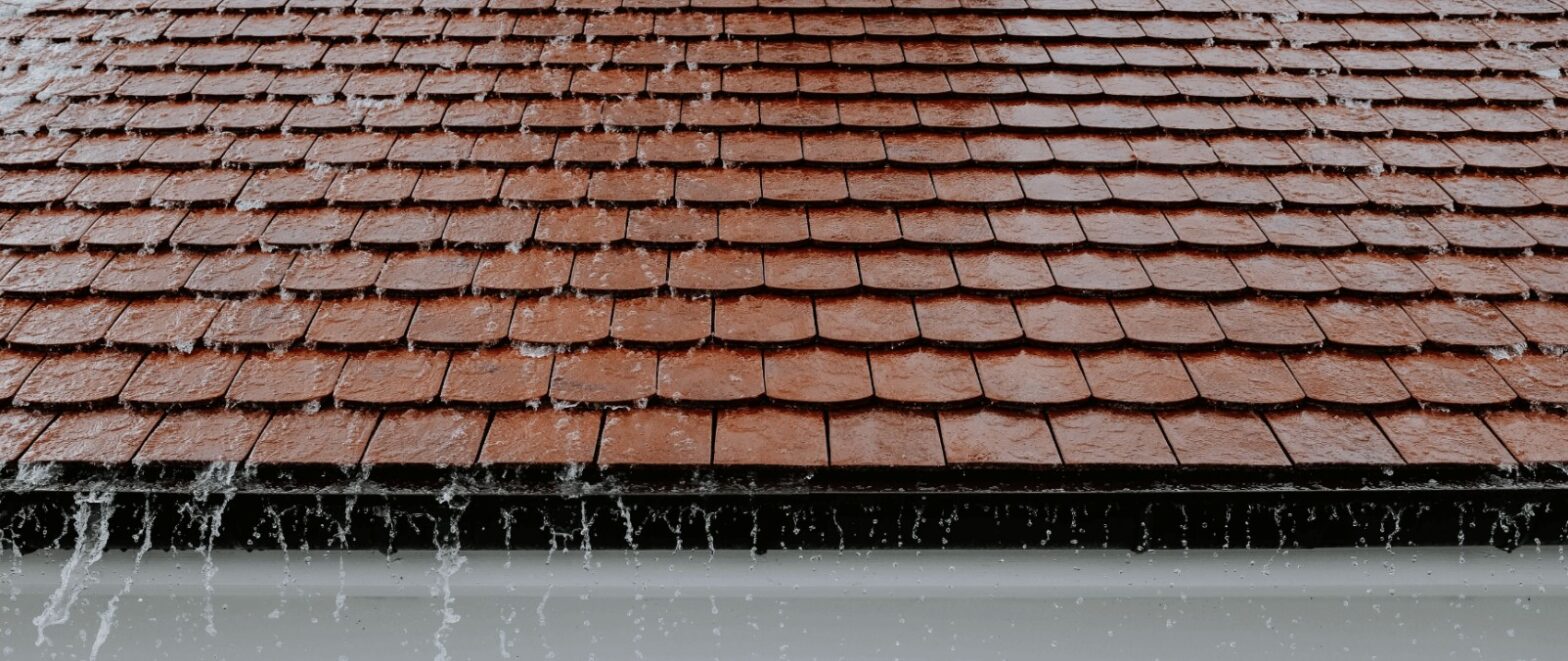
Preventing Moisture-Related Deterioration
Moisture intrusion threatens long-term building integrity and accelerates material deterioration, particularly in wood and metal elements. Even minor seepage can initiate structural damage and costly repairs without adequate water management.
Adequate protection begins with systems that prevent penetration and promote consistent drying.
Key Defences Against Water Intrusion
Successful moisture control relies on integrated design and precise installation. Several core components play a critical role in creating a water-resistant envelope:
- Correctly fitted vapour barriers beneath exterior cladding
- Strategically placed gutters and downpipes to manage runoff
- Pitched surfaces that direct water away from foundations
- Well-engineered flashing at windows and penetrations
- Ventilated wall assemblies that enhance airflow and drying
Building Endurance Through Layered Protection
Modern weatherproofing techniques safeguard the structure using multi-layered defence systems. Water-resistant wraps, drainage planes, and custom flashing details work together to manage water flow and protect key junctions.
These measures do more than deflect moisture—they actively guide it away from risk points, preserving the building’s stability over time.
Optimizing Requirements For Long-Term Sustainability
Accurate requirements gathering is critical from the outset of any construction project. Poor planning and vague specifications often lead to delays, costly revisions, and reduced project performance.
Studies show inadequate project definition accounts for 5.1% of total project waste. Effective planning begins with clearly defining stakeholder needs and identifying project constraints.
To ensure long-term success, practical requirements gathering should cover:
- Thorough documentation of building codes and regulatory standards
- Clearly defined sustainability objectives and performance indicators
- In-depth assessment of site conditions and environmental impacts
- Detailed material and system specifications
- Operational and maintenance requirements for long-term performance
Establishing accurate requirements early lays a solid foundation for sustainable construction. Including environmental factors from the beginning improves energy performance and reduces overall carbon output.
| Install impact guards and kick plates: Add stainless steel or composite kick plates and guards at door bases to protect against scuffs, impacts, and heavy equipment or strollers, maintaining appearance and integrity over time. |
Leveraging Ecodesign Principles For Enduring Impact
Eco-friendly architecture continues to redefine how buildings are designed for durability and efficiency. Long-lasting structures can better manage environmental stress while reducing their ecological footprint.
Sustainable materials and construction methods are critical in supporting building performance and occupant wellbeing, while conserving resources.
Durability-led solutions go beyond visual appeal. Using resilient materials and construction processes extends building lifespans, reduces waste, lowers maintenance costs, and conserves resources.
This design approach delivers lasting environmental and operational benefits for organisations and building users.
Practical principles guide the successful implementation of eco-design. These include:
- Use of renewable and recycled building materials
- Strategic positioning of weather-resistant components
- Energy-efficient systems that reduce consumption
- Adaptable spaces to meet evolving functional needs
- Durable finishes that require minimal upkeep
Green building strategies have consistently demonstrated increased operational efficiency and higher occupant satisfaction.
A durability-first approach, from the exterior entrance, builds resilient structures that retain function and appearance over time. These practices ensure long-term value while supporting environmental goals.
Lasting Design Matters
The challenge of creating durable, sustainable buildings that withstand time while protecting our environment has become increasingly crucial in modern architecture. Through thoughtful material selection, strategic planning, and innovative design approaches, we’ve discovered how to craft spaces that serve both present needs and future generations.
From resilient entryways to eco-conscious exteriors, the principles of durable design enhance building longevity and contribute to occupant wellbeing and environmental stewardship.