The importance of temperature control has never been clearer. Proper temperature management can significantly influence energy efficiency, comfort, and even the longevity of buildings.
As we seek to create spaces that meet modern standards, understanding how construction choices impact temperature control is vital. This article will explore various aspects of construction planning, materials, technologies, and practices that enhance temperature regulation.
Integrating Smart Insulation Solutions
Insulation material plays a pivotal role in maintaining stable indoor temperatures. Today’s market offers a variety of insulation options, each with its unique advantages. Traditional fiberglass has been a staple, but modern options like spray foam and rigid foam boards provide superior thermal performance. Spray foam, for instance, expands to fill gaps and cracks, significantly reducing air leaks. This approach leads to lower energy costs and improved comfort.
Environmental considerations are paramount. Many modern insulation materials are produced with sustainability in mind, using recycled content or less harmful chemicals. Opting for energy-efficient insulation helps meet regulations and appeals to eco-conscious consumers. Investing in high-quality insulation can result in fewer temperature fluctuations inside a home or building.
Incorporating insulation in the right places, like attics and walls, maximizes its effectiveness. However, consistently maintaining this insulation is equally important. Regular inspections ensure seals remain unbroken, providing optimal benefits year-round.
Utilizing Advanced HVAC Technologies
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems are fundamental for maintaining comfortable indoor conditions. Recent advancements in HVAC technology have revolutionized the way we approach temperature control in buildings.
Smart thermostats allow for real-time monitoring and adjustment of temperature settings according to usage patterns, leading to substantial energy savings.
The integration of variable refrigerant flow (VRF) systems offers several benefits by providing the ability to heat and cool different zones of a building independently. This improves comfort and optimizes energy use by directing energy only where it is needed. Adopting these technologies leads to a significant reduction in energy waste. Your HVAC system’s effectiveness greatly relies on proper installation and maintenance.
Ensuring that the system is designed according to the specific requirements of the building will enhance its performance. Regular tune-ups and updates with local experts ensure optimal operation, and, in the case of malfunction, having access to emergency heating repairs from local experts can mitigate downtime. Beyond VRF, geothermal heat pump systems represent a pinnacle of efficiency, leveraging the earth’s stable underground temperature to provide heating and cooling with remarkably low operational costs and a minimal environmental footprint.
The true potential of these systems is unlocked through building automation systems (BAS), which can integrate HVAC, lighting, and security into a single, intelligent network that optimizes energy use across the entire building based on occupancy and real-time utility pricing.
Choosing Energy-Efficient Windows
Windows are important in regulating indoor temperatures and managing energy consumption. High-performance windows shield against heat loss during winter and reduce heat gain in summer.
When selecting windows, look for features such as low-e coatings, which help reflect interior temperatures. Double or triple-glazing windows significantly enhance thermal performance, contributing to building energy efficiency.
Window placement affects natural lighting and airflow. Strategically placed windows harness natural breezes, reducing reliance on mechanical heating and cooling systems.
The incorporation of shading devices can minimize solar heat gain, preventing overheating in warmer months. Integrating these features creates an environment that remains comfortable while maximizing energy savings.
Investing in energy-efficient windows often qualifies building owners for rebates or tax incentives, making them financially appealing. Understanding the long-term benefits associated with these choices will result in a building that stands resilient against temperature variations, significantly minimizing energy costs.
Smart Building Materials for Temperature Regulation
When it comes to temperature control, the choice of building materials significantly impacts performance. Innovative materials designed with thermal mass properties can store and release heat as conditions change.
Materials like concrete and brick absorb heat during the day and release it at night, effectively stabilizing indoor temperatures. Reflective roofing materials can help keep buildings cool during hot weather by reflecting sunlight instead of absorbing it.
This reduces cooling costs and extends the lifespan of roofing components due to decreased heat stress. Choosing materials that promote energy efficiency plays a vital role in the sustainability of a building.
Materials made from recycled sources demonstrate environmental responsibility while enhancing a space’s temperature regulation capabilities.
Employing local materials often high in thermal mass properties can optimize cost efficiency while supporting local economies. In the construction industry, finding a balance between resource efficiency and performance leads to better temperature management.
Design Strategies for Natural Temperature Control
Architectural design is critical in achieving natural temperature control. Orientation of the building plays a significant role in maximizing sunlight and utilizing natural ventilation effectively. Designing with overhangs, awnings, and thermal mass features can drastically reduce energy consumption while maintaining comfort levels.
Green roofs and living walls offer innovative solutions as they enhance insulation and create natural cooling effects. The incorporation of landscaped spaces encourages improved air circulation, providing additional cooling during warmer months without relying heavily on mechanical systems.
Outdoor spaces can be designed to complement indoor environments. Strategically placed trees can provide shade and airflow, contributing to lower temperatures indoors. Utilizing these strategic design elements promotes environmental harmony while ensuring energy-efficient temperature control for the building.
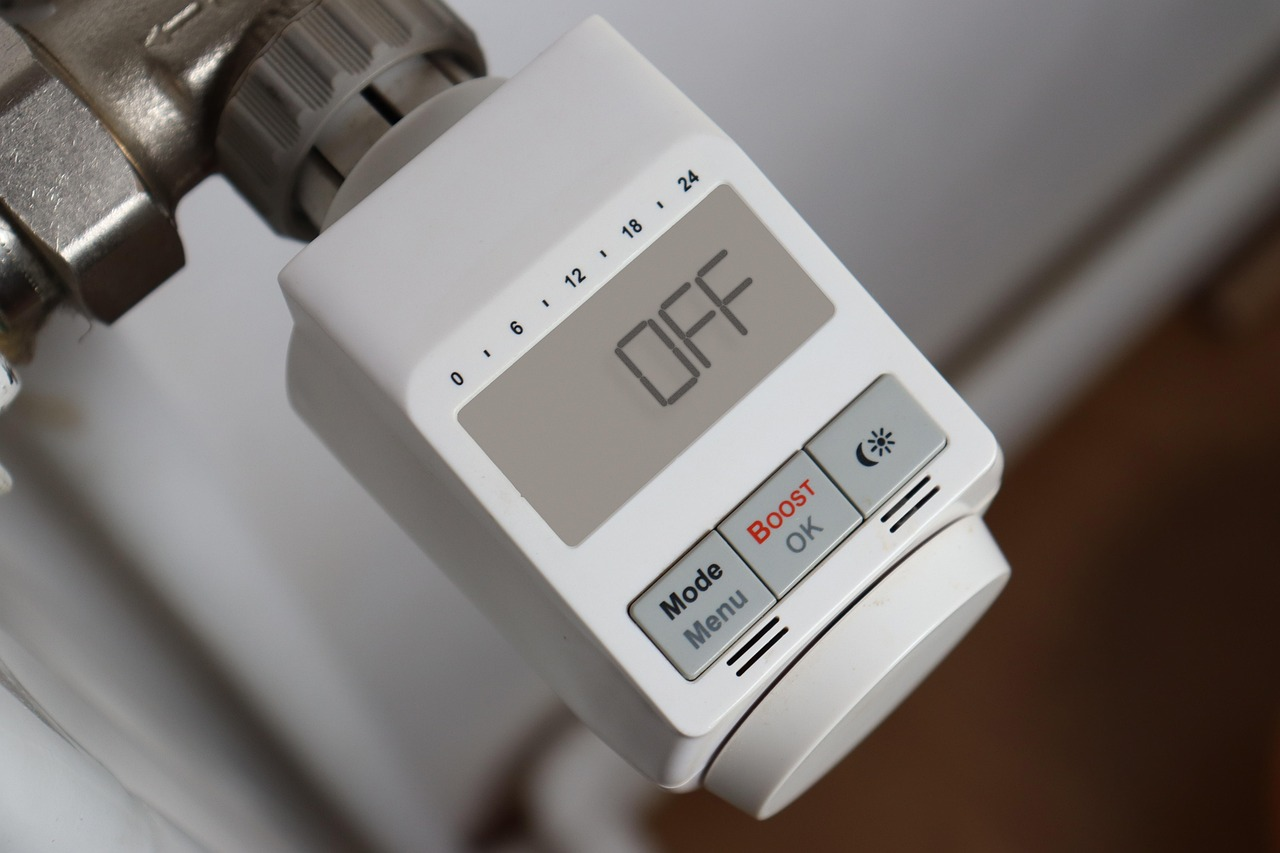

Regular Maintenance and Upkeep for Long-Term Efficiency
Regardless of the advanced technologies and materials chosen, regular maintenance is key to sustaining temperature control efficiency. Air filters should be changed regularly to ensure optimal airflow in HVAC systems, preventing strain on components and ensuring longevity. Seasonal checks help identify potential problems before they escalate into costly repairs.
Building owners can benefit from establishing a maintenance schedule that encompasses all temperature control systems, including heating, cooling, and insulation. Engaging with local experts can facilitate this process, ensuring that all necessary servicing occurs routinely, maintaining high performance throughout the year.
The objective is to create a continuous cycle of upkeep that enables buildings to adapt to the needs of occupants while remaining energy-efficient. Staying ahead of maintenance tasks guarantees reliable temperature control and helps avoid emergencies that can disrupt comfort and increase operating costs.
Smart construction choices significantly enhance temperature control within buildings. By integrating advanced insulation, energy-efficient windows, HVAC technologies, sustainable materials, design strategies, and a commitment to maintenance, building owners can create efficient, comfortable spaces.
Making informed decisions leads to reduced energy costs and improved living standards, reflecting a growing awareness of climate-conscious construction practices. By adopting these practices, we can create environments that are suitable for occupants and responsible towards our planet.